Dialog System¶
This software allows the Pepper robot to hold a human-like conversation in the SUTURO16 Project from the Institute of Artificial Intelligence -University of Bremen. The task of the robot in the project consists in taking care of the clients in a Cafe. The robot welcomes the clients, informs them about the Cafe services, takes their orders, forwards them to the robot baker and informs the clients on the evolution of their requests.
Architecture¶
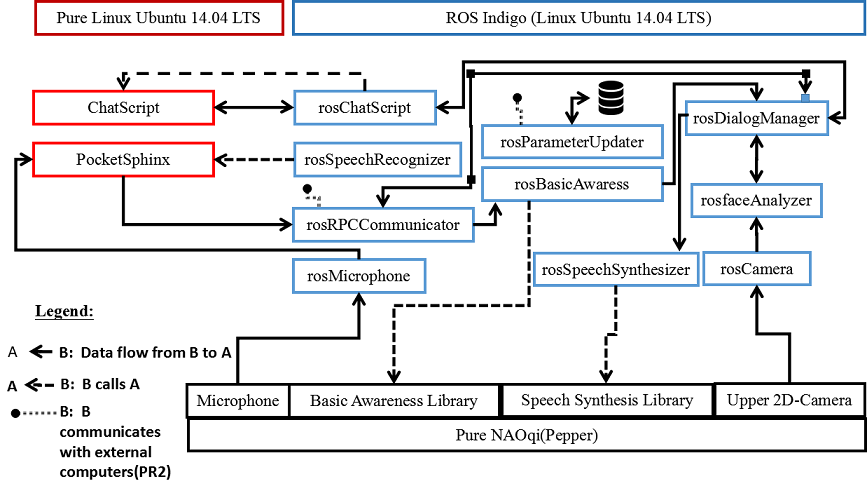
As we can see from the above architecture, the Dialog System is highly heterogeneous from the os perspective.
- NAOqi OS: operating system of the target robot(Pepper). Pure libraries were needed for robot control access.
- ROS Indigo: needed for a more efficient management of the Dialog System’s components and their intercommunication. Moreover, this packaging of components into ros nodes allows the Dialog System to interact with ROS environments. Just to recall that ROS Indigo is a virtual OS running on top of Linux Ubuntu.
- Linux Ubuntu 14.04 LTS: needed to run critical components which could neither be completely built from scratch, neither be appropriately adapted according to a chosen OS in the deadlines of the project. They could only be appropriately adapted to the project without changing the target OS to run them.
Consequently, the simplest way to launch the Dialog system consists in installing and running it remotely on any Linux Ubuntu 14.04 LTS platform.
Ros-based Image Streaming¶
This module is represented by the component rosCamera in the architecture and accessible at rosCamera.py. It samples images from the upper 2D-camera of Pepper, converts them into ROS images and publishes them over the ROS Image topic. The ROS parameters of this nodes are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- VIDEOMODE: indicates the position of the target camera. Value is local for a pc-webcam or remote for a robot camera
- PEPPERIP: indicates the Ip address of Pepper
- PEPPERPORT: indicates the port, Pepper should be accessed through
Face Recognition¶
This module is represented by the component rosfaceAnalyzer in the architecture and accessible at faceAnalyzer.py. It subscribes to ROS Image topic described above, detects faces based on Haar-like features described in haarcascadeFrontalfaceDefault.xml, introduces the detected faces into the dataset at faces and the detections into the folder detection. Then, it trains the classifier for face recognition from time to time with the data from faces. This module communicates with the Dialog Manager through suitably defined ROS messages, servers and actions accessible at dialogsystemMsgs. The ROS parameters of this nodes are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- CVRESET: indicates whether the module should be reinitialized at start or not. Value is off for volatile mode(all data lost on stop) and on for permanent mode(the model is preserved even on stop)
- PATH_TO_DATASET: absolute path to dataset folder. Any image must be saved with the format personName_id_instance.jpg. Example: franklin_1_3.jpg is the third image of the person having Franklin as name and 1 as Identification number.
- PATH_TO_DETECTOR: absolute path to detection folder
- CVTHRESHOLD: under this threshold, the recognized face is accepted
- CVRTHRESHOLD: under this threshold, the recognized face is considered as resemblance. Over this threshold, the recognized face is ignored
- CVFACEWINDOW: the minimal size of the side of the square, a detected face can fit in
- CVDIMENSION: length of the image after pca-based compression(number of dimensions retained)
- CVNEIGHBOR: minimal number of meaningfull objects that should be detected around a presumed detected face before the latter is accepted
- CVSCALE: for scaling images before applying the detector, because The detector was trained on fixed-size images
- CVSCANFREQUENCY: for consistent visualization, a moving average with a window of size CVSCANFREQUENCY over the image stream takes place
- CVINSTANCEFREQUENCY: maximal number of images to save per face when detected
- CVIDIMENSIONDEFAULT: default size of the side of the square, each detected face should fit in
- CVIDIMENSION: size of the side of the square, each detected face should fit in. Same as CVIDIMENSIONDEFAULT, but dynamic because inferred from the available sizes of faces in the dataset.
Speech Recognition¶
This module is represented by the component rosSpeechRecognizer in the architecture and accessible at sphinxAsr.py. It sets the parameters of the pure c++ module PocketSphinx and starts it. PocketSphinx receives Speech from a Gstreamer-TCP-server, recognizes it and then publishes the result for further processing. It is accessible at continuous.cpp and was derived from CMUSphinx. The ROS parameters of this nodes are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- ASRCWD: path prefix to access PocketSphinx
- MLLR: base path to access the speaker adapter of the speech recognizer. Allows online adaptation to speaker
- HMM: base path to access the acoustic model of the speech recognizer
- ASRPATH: base path to access the speech recognizer’s object file
- TRESHOLD: the decoded speech is only considered under this threshold
- DATAPATH: base path to access the dictionary and language models of the speech recognizer
- NBTHREADS: the number of instances of speech recognizer to execute simultaneously and then combine their results into a more accurate one. It allows an ensemble learning-based recognition
- BEAMSIZE: only the BEAMSIZE best results from the NBTHREADS available must be combined to get the final result
- INDEX: this parameter is a positive integer and is used for naming of dictionary and language models. Example: NBTHREADS = 2 and INDEX = 33, then the folder DATAPATH will contain the files pepper33.dic(dictionary model of first thread/instance), pepper33.lm, pepper34.dic, pepper34.lm(language model of second thread)
- HOST: IP address of the underlying computer
- PORT: port of the Gstreamer-TCP-server
- RPCPORT: port of the RPC server, the decoded speech will be sent to
- ORDER: used to synchronize starts of Gstreamer-TCP-client and Gstreamer-TCP-server. while value is 0, the Gstreamer-TCP-client must wait for Gstreamer-TCP-server to start
Gstreamer-based Audio Streaming¶
This module is represented by the component rosMicrophone in the architecture and accessible at gstreamerSphinx.py. It configures and starts a Gstreamer-TCP-client on Pepper, which receives audio samples from the microphone of Pepper and sends them regularly to the Gstreamer-TCP-server described above for decoding into text. The ROS parameters of this nodes are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- RHOST: indicates the IP address of the host, which the Gstreamer-TCP-client runs on. Pepper’s IP by default
- RPORT: indicates the port, which the SSH service for launching the Gstreamer-TCP-client can be accessed through
- RUSERNAME: indicates the username of the user accessing the ssh service on the robot
- PASSWORD: indicates the password of the user accessing the ssh service on the robot
- HOST: indicates the IP address of the host, which the Gstreamer-TCP-client is running on
- PORT: indicates the port, which the Gstreamer-TCP-server is listening to
- ORDER: used to synchronize starts of Gstreamer-TCP-client and Gstreamer-TCP-server. while value is 0, the Gstreamer-TCP-client must wait for Gstreamer-TCP-server to start
Basic Awareness¶
This module is represented by the component rosBasicAwareness in the architecture and accessible at speechRecognizer.py. It starts a pure NAOqi empty behavior as proxy on Pepper to get a total robot control, launches some services from the robot libraries to guarantee the basic awareness(stimuli tracking, Human detection, breathing), receives decoded speech from the RPC-server and forwards it to the dialog manager for further processing. The ROS parameters of this nodes are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- PEPPERIP: indicates the IP address of the robot Pepper
- PEPPERPORT: indicates the port, which Pepper is accessed through
- NAOQIPACKAGEUUID: indicates the identification number of the empty behavior on the robot
- PATHTOBEHAVIOR: indicates the path to the empty behavior given NAOQIPACKAGEUUID on the robot
- busy: used to clearly distinguish the speaking phases from the hearing phases of the robot. If value is 1(robot is speaking), then rosBasicAwareness ignores results from speech recognizer. reset to 0 after speaking
ChatScript¶
This module is represented by the component rosChatScript in the architecture and accessible at dialogCoreServerManager.py. It starts and interacts with the ChatScript platform accessible at ChatScript. The ChatScript platform is a text-based natural language processing toolkit. It provides us with a language to completely specify the core of the Dialog System(understanding, dialog flow control, answer generation ) and a server-like interpreter of those specifications. In the Dialog System’s pipeline, rosChatScript acts like a bridge between the speech recognition and the speech synthesis through the dialog manager. The ROS parameters of this nodes are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- CORESERVERIP: indicates the IP address of the host, which the server-like interpreter of ChatScript runs on
- CORESERVERPORT: indicates the port, which the server-like interpreter is accessed through
- CORESERVERCWD: indicates the absolute path to ChatScript’s folder
- CORESERVERPATH: indicates the relative path from CORESERVERCWD to ChatScript’s object file
- PATH_TO_USERDIALOGDATA: indicates relative path to dialog-related user data’s folder
Dialog Management¶
This module is represented by the component rosDialogManager in the architecture and accessible at dialogManager.py. It serves as router to all other components for their connections and communications. The module has currently no ROS parameters at dialog.launch.
Speech Synthesis¶
This module is represented by the component rosSpeechSynthesis in the architecture and accessible at naoSpeech.py. It receives textual outputs from the rosDialogManager module and then calls pure NAOqi libraries to synthesize speech from the input text. The ROS parameters are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- PEPPERIP: indicates the IP address of the robot Pepper
- PEPPERPORT: indicates the port, which Pepper is accessed through
- busy: used to clearly distinguish the speaking phases from the hearing phases of the robot. If value is 1(robot is speaking), then rosBasicAwareness ignores results from speech recognizer. reset to 0 after speaking
RPC-Client¶
This module is the client part of the component rosRPCCommunicator in the architecture and accessible at rpcClient.py. It directly receives from a topic requests published by the dialog manager and forwards them through RPC calls to the robot PR2. The ROS parameters are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- PR2IP: indicates the IP address of the robot PR2
- PR2PORT: indicates the port, which PR2 is accessed through
RPC-Server¶
This module is the server part of the component rosRPCCommunicator in the architecture and accessible at rpcServer.py. On the one hand, It directly receives textual outputs from the speech recognition, then retrieves from the received text structured information thank to the Dialog System’s utility component and forwards the structured information to the rosBasicAwareness module. On the other hand, it receives feedbacks from the robot PR2 and forwards them to the dialog manager. The ROS parameters are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- RPCSERVERIP: indicates the IP address of the host, which this server runs on
- RPCSERVERIPPORT: indicates the port, which this server is accessed through
- FOLDER: indicates the absolute path to the dataset (set of sentences, expressions and words) for speech recognition
Network Parameter Update¶
This module is represented by the component rosParameterUpdater in the architecture and accessible at netparamupdater.py. It sleeps and wakes up at regular intervals of time to silently update network parameters(changing permanently) such as IP addresses and ports of hosts and programs taking place in the whole project SUTURO from the inside environment(Dialog System, Pepper) as well as from the outside environment(Perception, Planning, Knowledge, Manipulation, PR2). It presents RPC-server-like and RPC-client-like functionalities to send and receive updates. The updates do not require any restart of the programs or computers. The ROS parameters are accessible at dialog.launch and follow:
- PR2IP: indicates the IP address of the robot PR2
- PR2PORT: indicates the port, which PR2 is accessed through
- PEPPERIP: indicates the IP address of the robot Pepper
- PEPPERPORT: indicates the port, which Pepper is accessed through
- RPCSERVERIP: indicates the IP address of the host, which this module runs on
- RPCSERVERIPPORT: indicates the port, which this module is accessed through
Utility¶
This module acts as proper library of the Dialog System and is accessible at utility.py. It provides the above described components with a set of mathematical functionalities. It generates several datasets(set of sentences, expressions and words) from a single dataset in order to implement an Ensemble-Learning technique for speech recognition. Moreover, it implements a vector space classifier for information retrieval during the speech recognition and a couple of encoding-decoding algorithms for a bijection NxN to N. The module has currently no ROS parameters at dialog.launch.
Prerequisites, Installation and Start¶
As prerequisites,
- Linux Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 64bits
- Python 2.7 64bits
- ROS Indigo
To install,
- Create a general workspace folder and name it as you want. Let say Dialog
- Clone the pepper-dialog’s git repository in the general workspace folder Dialog
- Copy the installation file installer.sh of the pepper-dialog’s repository to the general workspace folder Dialog
- Download the package pynaoqi SDK version 2.5.5.5 from the Aldebaran-Softbank Robotics’s website. You may need to create a user account before downloading the tar.gz package. The download folder must neither be pepper-dialog nor inside it.
- Open the file installer.sh in Dialog and set the environment variable PYTHON_NAOQI_TAR_GZ_PATH to the above downloaded package’s absolute file path
- Download and install Choregraphe version 2.5.5.5 from the Aldebaran-Softbank Robotics’s website.
- Install the pure NAOqi package suturo16-0.0.0.pkg on Pepper robot using Choregraphe 2.5.*
- Run the installer: ./installer.sh
To start,
- Make sure the parameters are correctly set at dialog.launch. The Ip addresses and ports should be imperatively adapted.
- run the launcher located in folder Dialog/pepperdialog: ./launcher.sh